7.06 Cell Biology#
- 7.06 Cell Biology
- Definitions
- Techniques
- 1. Why is cell biology exciting? Questions and techniques
- 2. Compartmentalization: the membrane system
- The lipid bilayer
- Phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and sterols are the major lipids in cell membranes
- Phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers
- The lipid bilayer is a two-dimensional fluid
- The fluidity of a lipid bilayer depends on its composition
- Despite their fluidity, lipid bilayers can form domains of different compositions
- Lipid droplets are surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer
- The asymmetry of the lipid bilayer is functionally important
- Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic plasma membranes
- Membrane proteins
- Membrane proteins can be associated with the lipid bilayer in various ways
- Lipid anchors control the membrane localization of some signaling proteins
- In most transmembrane proteins, the polypeptide chain crosses the lipid bilayer in an -helical conformation
- Transmembrane -helices often interact with one another
- Some -barrels form large channels
- Many membrane proteins are glycosylated
- Membrane proteins can be solubilized and purified in detergerents
- Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven proton pump that traverses the lipid bilayer as seven -helices
- Membrane proteins often function as large complexes
- Many membrane proteins diffuse in the plane of the membrane
- Cells can confine proteins and lipids to specific domains within a membrane
- The cortical cytoskeleton gives membranes mechanical strength and restricts membrane protein diffusion
- Membrane-bending proteins deform bilayers
- The lipid bilayer
- 3. Getting molecules across membranes
Definitions#
Techniques#
1. Why is cell biology exciting? Questions and techniques#
@2022-09-07
2. Compartmentalization: the membrane system#
@2022-09-12
- Readings
- Alberts/5e, Chapter 10
The lipid bilayer#
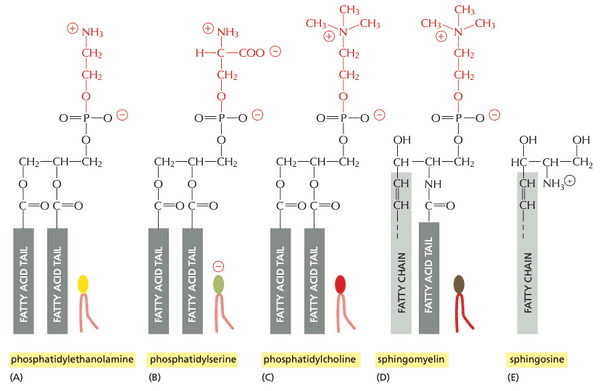
Phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and sterols are the major lipids in cell membranes#
- phospholipids are the most abundant membrane lipids; composed phosphate with two hydrocarbon tails
- phosphoglycerides. subset of phospholipids that have a glycerol backbone
- sphingolipids. phospholipids built from a sphingosine backbone rather than a glycerol backbone
- phosphotidylserine is the only phospholipid with a net negative charge at physiological pH.
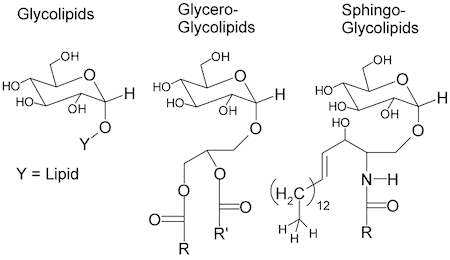
- glycolipids ( phospholipids). resemble sphingolipids but have sugars attached rather than phosphate-linked head groups
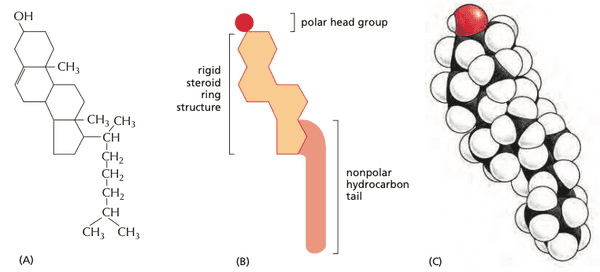
- eukaryotic plasma membranes have lots of cholesterol; almost 1 molecule for every phospholipid molecule
- cholesterol orients itself so that its polar head is adjacent to polar heads of phospholipid neighbors.
Structure of four major phospholipids in mammalian plasma membranes. Also includes a structure of sphingosine (the backbone of sphingolipids phospholipids).
Phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers#
- hydrophobic molecules group together in aqueous solution because the process of forming organized cages around the hydrophobic molecules decreases entropy (increases free energy), so free-energy cost is minimized if the surface area is minimized (which is accomplished when the hydrophobic molecules are grouped).